ONLINE VOTING SYSTEM
ONLINE VOTING SYSTEM
1.1 GENERAL
The aim of the project
is to create and manage polling and election details. This is a system which enables all citizens to
cast their vote online. Increasing the voting
percentage across the country is the major goal of this project. People have to visit the booth to cast their vote in the
present system across the country. This system is online and hence even people
who live out of their home town can also vote. Database of all the eligible
citizens and candidates are maintained by the system.
Online voting system gathers its own significance since the NRI voting Rights bill have been passed by the parliament on Feb 11 ,2011. . The new law will allow an Indian citizen residing abroad to enroll in voter’s list and exercise his franchise even if he or she remained away from place of residence in India for more than six months owing to employment, education or otherwise. In the present case the person should be present within the constituency on the day of polling for exercising his right to vote.
Thus our project,
online voting should enhance the opportunities of voters outside the country to
vote for their nation on implementation.
1.2.
COMPANY PROFILE
Focuz Infotech is a fast growing
Linux Software company having an Impressive track record in Developing,
Implementing and supporting high end Innovative technology solutions right from
its take off in 1998.
We
are a highly recognized national technology company, having our own dedicated
R&D and Consulting divisions supported by an excellent blend of visionary
consultants consists of Management and technology Professionals, who holds
Sheer Confidence , Dedication, Exposure, experience and commitment for
inventing and implementing ideal technical solutions. We have a large no of
customers from various business domains spread across the country. We are in
the technology business to ensure our customers satisfaction, further,
promoting our innovative products globally through collaborations and determined
to grow global.
Focuz
Infotech is an ever-expanding IT Consultancy Company promoted by Focuz
innovations (Pvt) Ltd, India, backed up by Focuz Group ,established in 1978 , A
Rs. 2500 million, highly reputed, multifaceted corporate focused to Information
Technology, Automobiles and Tourism. For more information, Plz visit www.focuz.co.in
Focuz Infotech started its IT initiatives in the
year 1998, initially concentrating on Oracle based solutions and further to
UNIX and Linux Technologies in a big way.
Focuz
Infotech owns world-class 24/7 capable 15000 sq. Ft. Linux Research and
Development unit in Kochi, a beautiful Island in Kerala, the God's own country.
1.3. INTROUCTION TO TOOLS
1.3.1. LINUX
Linux is an operating system, a
software program that controls your computer. Most vendors load an operating
system onto the har d drive of a PC before delivering the PC.
Linux is distinguished from many
popular operating systems in three important ways:
Linux is a
cross-platform operating system that runs on many computer models. Only UNIX,
an ancestor of Linux, rivals Linux in this respect.Linux is free, in two senses. First,
you may pay nothing to obtain and use Linux. On the other hand, you may choose
to purchase Linux from a vendor who bundles Linux with special documentation or
applications, or who provides technical support. However, even in this case,
the cost of Linux is likely to be a fraction of what you'd pay for another
operating system. So, Linux is free or nearly free in an economic sense.
ADVANTAGES OF LINUX
Linux
source code is freely distributed. Tens of thousands of programmers have reviewed
the source code to improve performance, eliminate bugs, and strengthen
security. No other operating system has ever undergone this level of review.
This Open Source design has created most of the advantages listed below.
Linux
has the best technical support available. Linux is supported by commercial distributors,
consultants, and by a very active community of users and developers. In 1997,
the Linux community was awarded InfoWorld's Product of the Year Award for Best
Technical Support over all commercial software vendors.
Linux
has no vendor lock-in. The availability of source code means that every user and support
provider is empowered to get to the root of technical problems quickly and
effectively. This contrasts sharply with proprietary operating systems, where
even top-tier support providers must rely on the OS vendor for technical
information and bug fixes.
Linux
runs on a wide range of hardware. Most Linux systems are based on standard PC
hardware, and Linux supports a very wide range of PC devices. However, it also
supports a wide range of other computer types, including Alpha, Power PC, 680x0,
SPARC, and Strong Arm processors, and system sizes ranging from PDAs
Linux
has the tools and applications you need. Programs ranging from the market-dominating
Apache web server to the powerful GIMP graphics editor are included in most
Linux distributions. Free and commercial applications meet are available to
meet most application needs.
Linux
interoperates with many other types of computer systems. Linux communicates using
the native networking protocols of Unix, Microsoft Windows 95/NT, IBM OS/2,
Netware, and Macintosh systems and can also read and write disks and partitions
from these and other operating systems.
Linux
has a low total cost of ownership. Although the Linux learning curve is
significant, the stability, design, and breadth of tools available for Linux
result in very low ongoing operating costs.
Linux:
all for one and one for all?? All changes one makes in Open Source software
will benefit each and everyone, all over the world. Without exceptions or
constraints.
1.3.2. JAVA
Java is an object oriented, platform independent
programming language, which has become inseparably linked with the online
environment of the internet. Java had a profound effect on the internet. The
reason for this is quite simple. Java expands the universe of objects that can
move about freely in cyberspace. Java achieves security by confining a java
program to the java execution environment and not allowing it access to other
parts of the computer. Java provides an elegant and efficient mechanism for attaining
portability.
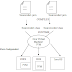
The java virtual machine specification defines JVM as:
An imaginary machine
that is implemented by emulating it in software on a real machine. Code for the
JVM is stored in the .class files, each of which contains code for at most one
public class. Its represented as in fig1.
The java virtual machine specification provides the
hardware platform specifications to which we compile all java technology codes.
This software enables the Java software to be platform – independent because
the compilation is done for a generic machine, known as the JVM.
Fig:1.3.3 Java Technology
1.3.3.
JAVA BEAN
A Java Bean is a server-side component that helps the
server side programs to be split into small manageable pieces. A Java Bean has
a set of properties that can be changed or read. It is also possible to find
out the properties that a bean has available. Two things make Java Beans
useful. The first is that neither Java programmers nor JSP programmers need to
know anything about a bean in advance in order to use it.
The second useful
thing is that it does not matter how they go about manipulating their
properties. Thus Beans act as mysterious black boxes with switches and
read-outs.
There are three kinds of enterprise beans: session
beans, entity beans, and message driven beans. Enterprise
1.3.4
JAVA SERVER PAGES
Java Server Pages technology is the Java platform
technology for building applications containing dynamic Web content such as
HTML, DHTML,, XHTML, XML. The Java Server Pages Technology enables the
authoring of web pages that create dynamic content easily but with maximum
power and flexibility. This technology lets you put snippets of servlet code
directly into a text based document.
The Java Server Pages technology offers a number of advantages
·
Write Once , Run Anywhere properties
·
High quality tool support
·
Reuse of components and tag libraries
·
Separation of dynamic and static content
·
Support for scripting actions
·
Web access layer for N-tier enterprise
application architectures.
JAVA
SERVELET TECHNOLOGY
Java servlet technology let us to define HTTP-specific
servlet classes. Servlet class extends the capabilities of servers that host
applications accessed by way of a request-response programming model. Although
servlet can respond to any type of request , they are commonly used to extend
the applications hosted by web servers.
Fig1. 3.2:
Execution of Java Servlet
The Java Script is a commonly used scripting language
for HTML pages. The scripting languages are mainly used for client side
validation purpose. As we know the scripting statements are sent to the client
machine and executed there during the client operations, it reduces the work
load of server. The other features are:
·
It has procedural capabilities,
·
Platform independent
·
Low disc space needed
·
Easy debugging and testing
·
1.3.5
HTML
It is a language used for the specification of
structural markup. HTML give the web authors the means to publish online
documents with headings,texts,tables,lists,photos,etc.HTML is used in our
program to create forms in the server side for entering, updating and viewing
the server applications in a user friendly environment.
1.3.6 JDBC
JDBC is a Java API for executing SQL statements. It
consists of classes and interfaces written in the Java Programming language.
JDBC provides a standard API tool for database developers and make s it
possible to write database applications using a pure Java API.
Using JDBC, it is easy to send SQL statements to
virtually any relational database. One can write a single program using JDBC API,
and the program will be able to send SQL statements to the appropriate
database. The two tier jdbc modelis as given below:
Fig:
3.3 The two-tier JDBC model
JDBC makes it possible to do three things as follows:
·
Establish a connection with database
·
Send SQL statements.
·
Process the results.
1.3.6
MYSQL
MySQL provides our small, medium and large enterprise
customers with affordable, open access to their web data warehouses. MySQL
allows us to offer our System Administrator low cost, low maintenance database
solution for applications without sacrificing power, performance or
scalability.
Benefits of MySQL are as follows:
§ Easy
to maintain & upgrade, does not have a slew of administrative tasks to
put up.
§ Its
table format does not vary between releases
§ It
has cleanly separated table handler modules and can mix access to different
type of tables.
§ It
seems to be developed iteratively, and the features are very stable when they
ship them.
It is a relational database. Over the past several
years, this relational database management systems have become the most widely
accepted way to manage data.
It offers benefits such as:
§ Easy
to access data
§ Flexibility
in data modeling
§ Reduced
data storage and redundancy
§ Independence
§ A
high level data manipulation language
REQUIREMENT
SPECIFICATION
Requirement Specification is the part
of the project which gives the details about the hardware and software
requirements of our project. It also details the features of the programming
language used.
2.1 HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS
In order to implement a new system the
choice of processor with maximum possible speed is made. There should be
sufficient memory to store data and software tools for efficient processing.
System : IBM-Compatible PC
Processor
: Pentium IV
Speed : 2.0 GHz
Memory :
256 MB RAM
Hard Disk Drive : 40 GB
2.2 SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS
Platform :
Linux
Language used :
J2EE
Back end :
My SQL
Technologies used :
JSP, JDBC
Designer tool : HTML
Server : Apache tomcat 5.5.9 To develop application
software, we use different types of software. The software for the development
has been selected based on several factors such as:
- Support
- Cost Effectiveness
- Development Speed
- Ability to create robust application least time
- Stability
SYSTEM
ANALYSIS
AND
DESIGN
3. SYSTEM ANALYSIS
System analysis is the process of
gathering and interpreting facts, diagnosing problems and the information to
recommended improvements on the system. System analysis is a problem solving
activity that requires intensive communication between the system users and
system developers. System analysis or study is an important phase of any system
development process. The system is studied to the minutest detail and analyzed.
The system analyst plays the role of the
interrogator and dwells deep into the working of the present system.
The system is viewed as a whole and the input to the system are identified. The
outputs from the organizations are traced to the various processes.
A detailed study of the process
must be by various techniques like interviews, questionnaires etc. The data
collected by these sources must be scrutinized to arrive to a conclusion. The
conclusion is an understanding of how the system functions. This system is
called existing system. Now the existing system is subjected to close study and
problem areas are identified. The designer now functions as a problem solver
and tries to sort out difficulties that the enterprise faces. The solutions are
given as proposals. The proposal is then weighed with the existing system analytically
and the best one is selected. The proposal is presented to the user for an
endorsement by the user .The proposal is reviewed on user request and suitable
changes are made. This is loop that ends as soon as the user is satisfied with
proposal.
3.1 EXISTING SYSTEM
In the present system the is
no such application level system provisions in the country to carry out the
voting and procedure as a whole . Also in the present status, there is no such
application in use for automated system for voting according to the voting
structure existing in the country. All the step by step procedures are carried
out by the authorized authorities according to the jobs assigned by the ECI.
The fact is all the procedures are carried out manually, starting from the
registration process to result publishing.
The government to do this process
manually wastes a lot of time and money. Thus the present system proves itself
to be an inefficient one. The existing system is not web based. The user or
person must want to go to the polling station for casting their votes.
3.2 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The new implemented voting protocol has two
main players: The voter and administrator sections. The voter(which can be
found at home, in a working station, in a special polling station or any other
device have the fuction of performing the Authentication and voting).The
administrator performs the function of voter and candidate registration,
authorization and validation of voter, database and counting and the result.
The main
advantages of the new protocol are the following:
1) Public transparency by the
administrator (publication of Voter ID key, etc.).
2) Inured to technical troubles like
interruption of access, etc, uncomplicated recovery.
3)Possibility of configuration for
different voting models by policies and Greater performance.
Furthermore it
is assumed that a trustworthy Administrator is available. Apart from that, the
accessibility to the public in the
voting procedure plays a special role, which means that the voting result can
be monitored, although casting of the votes has to be secret as a matter of
course.
Accessibility to
the public is necessary for all voting stages and is performed by the electoral
committee, but also by any member of the public.
3.3 DATA FLOW DIAGRAM
A data flow diagram (DFD) is a graphical
representation of the “flow” of data through an information system. A data flow
diagram can also be used for the visualization of data processing (structured
design). It is common practice for a designer to draw a context-level DFD first
which shows the interaction between the system and outside entities. This
context-level DFD is then “exploded” to show more details of the system being
modeled.
Data
flow diagrams were invented by Larry Constantine, the original developer of
structured design, based on Martin and Estrin’s “data flow graphs” model of
computation. Data flow diagrams (DFD’s) are one of the three essential
perspectives of Structured System
Analysis and Design Method SSADM. The sponsor of the project and the end users
will need to be brief and consulted through out all stages of a system’s
evolution. With a data flow diagram users are able to visualize how the system
will operate, what the system will accomplish, and how the system will be
implemented. The old system’s data flow diagrams can be drawn up and compared
with new system’s data flow diagrams to draw comparisons to implement a more
efficient system. Diagram
Elements of a DFD
There
are 4 key elements in a Data Flow diagram, Processes, Data Flows, Data stores,
and external entities.
Table3.1.Elements of DFD
The
Process entity identifies a process
taking place, it must have atleast one input and output. A process with no
input is known as “miracle process”. An output is a “black hole process”. Each
process has the following:
A Number,A Name
(verb phrase),A Description,At least one input,At least one output
The
Data Flow entity identifies the flow
of data between processes, data stores and external entities. A data flow
cannot connect an external entity to a data source, at least one connection
must be with a process. There are also “physical” flows, i.e. those that use a
physical medium, like a membership card. Each data flow has the following:
A name (Noun),A
Description ,One or more connection to a process
The
Data Store entity identifies stores
of data, both manual and electronic. Electronic or “digital” stores are
identified by the letter D, and manual filing systems by the letter M. Each
data store has the following:
A numberA name,A
description, One or more input data flows,One or more output data flows
The
External Entity identifies external
entities which interact with the system, usually clients but can be within the
same entity, e.g. the same doctor shown twice on the same diagram can be
identified by a horizontal line in the top left corner of the symbol. Each
external entity has the following:
A Name (Noun),A
Description
3.4. SYSTEM DESIGN
System Design’s main aim is to
identify the modules that should be in the system, the specifications of these
modules and how they interact with each other to produce the desired results.
At the end of system design all the major data structures, file formats and the
major modules in the system and their specifications are decided.The most
creative and challenging phase of the system development process is design
phase, it is a solution, a “how to” approach to the creation of the proposed
system Design, the first step in the development of an engineered product is
initiated only after a clear exposition
of expected product functions becomes available. Based on the user requirements
and the detailed analysis of a new system, the new system must be designed.
This is the phase of system designing. Normally the design proceeds in two
stages: preliminary or general design, structure or detailed design.
Preliminary or general design: In the
preliminary or general design, the features of
the new system are specified. The costs of implementing these features
and benefits to be derived are estimated. If the project is still considered to
be feasible, we move to detailed design stage.
Structure or detailed design: In
the detailed design stage, computer oriented work begins in the earnest. At
this stage, the design of the system becomes more structured. Structured design
is a blue print of a computer system solution to a given problem having the same components and inter-
relationship among the same components as the original problem. Input, output
and processing specifications are drawn up in detail .In the design stage, the
programming language and the platform in which the new system will run are also
decided. There are several tools and techniques used for designing.
Simple designs are easily
understood, easily built, and easily tested. Simplicity is the most important
criteria of a design. Other design criteria include the following:
Documentation: A good design always
comes with a set of well-written documents.
Testability: In a good design, every
requirement is testable. A design that cannot be easily tested against its
requirements is not acceptable design.
Structure: A good design presents
hierarchical structure that makes logical use of control policies among
components.
Modularity: A good design is modular
and exhibits the properties of high cohesiveness and low coupling.
Representation: A good design should be
easily communicated to all interested parties through appropriate abstraction
and representation.
Reusability: a good design should be
repeatable and reusable.
3.4.1.
MODULE DESIGN
The proposed system consists of two
modules,
- Administrator Module
- User Module
USER (VOTER) MODULE
User interface consists of a login name and
unique password using which he/she can login into the Online Voting System.
This will be supplied by the administrator to the user. Once the user has
logged in, he has the privilege to view the names of the candidates listed by
the administrator, view the results after the termination date of the election.
The user module constitutes only one sub module:
Authentication & Voting
•
Each voter is provided with unique username and
password manually by the administrator. The voter uses the username and
password for login and exercise the fundamental right of voting. if incorrect
username and password entered, the access to is denied to the user. And also
voter is allowed to vote only once. This
is the security feature provided against external access of the system.
•
After login the voter enters the voter home page ,which provides the links :
Candidate List
This facilitates the voter to view the candidate
names, the constituency name, their symbol and their party name.
Vote
This provides the voter with
a list of candidate with in his/her constituency along with selection option
(radio button) to select the preferred candidate from the list. If the voting
date is before termination date, the vote goes valid else goes invalid.
View Results
This
provides graphical and user friendly representation of the votes obtained by
each candidate. It includes the percentage of the votes obtained by each candidate.
But the result can be viewed only after the termination date of the election.
Logout
This
provides an option for the voter to quit the session ,while in the voter home
page.
ADMINISTRATOR
MODULE
Administrator interface consists of a login
name and unique password using which admin can login into the Online Voting
System. Administrator has the main control of the system. By logging into the
page it can perform the following tasks.
Add
Candidate
Here
the admin can add the list of candidates in the election. It includes
candidates name, address.gender,party, party symbol etc. The candidates will be
added to the list only after completing the procedures.
Add
Voter
Here the voters can be added to the database. The voters have also the
privilege to check the voters list from the homepage. The voters details
includes name, address, gender, age, constituency, image etc.
Add
Election
Here
the election to be conducted is selected. To add an election the constituency
should be selected and termination date of election should be specified.
Add
Constituency
The
constituency that is going to conduct election should be selected.
Voters List
Here
we can view the voters list. Each constituency will be having separate voters
list.
Candidate
List
The
list of candidates participating in the election can be seen. It includes the
candidates name, party name and party symbol.
The sub-modules of administrator are:
Ø Voting Structure,
Ø Voters Registration
Ø Candidate Registration
Ø Counting & Categorization of Results
Voting
Structure
Here the
eligible voters who are permitted to login to the system can utilize the right
to vote. Each voter can register a single vote to a candidate’s favour in
his/her constituency. The security measures taken within the system prevents
them from exercising their votes again i.e. the second vote by the same user
goes invalid. The starting and ending dates of the election are specified by
the administrator. The user must have an identity card and he must be in voters
list.
Voters Registration
The
registration procedure of all the eligible voters .This registration process is
done by the administrator. According to voters database each voter is provided
with a unique identification codes which includes username and password.
The details of
the voters include username, password, name, address, gender, constituency,
image etc.With the voter registration, thus producing the voter list with the
given information of the voters. The voter list can be viewed by anyone
accessing the webpage. The admin can view the voter list with in his homepage.
Candidate Registration
The
registration of the candidates in each constituency is done by the
administrator. The details of the candidate includes name, address, gender
,his/her constituency, party and image.
With the candidate registration, thus producing the candidate list with the
given information of the candidates. The candidate list can be viewed by admin
and the vote within their respective homepages. According to candidates
database (manual) each details of the
candidates are stored in database controlled by the admin including candidates
details.
Counting & Categorization of Results
When the voter votes, the number of
votes obtained by the selected candidate is incremented by 1.The result is
published only after the voting process is over. It is accessible from the next
day after the termination date. Here we depict the result in the graphical
representation according to the percentage of vote obtained by the candidate.
Result can be viewed by everyone who visits into the site without any
authentication problem. A link to view the result is kept in the index
page and both admin and voter can view the result in their respective homepages.
When the user clicks the “RESULT” link, before the termination date of the
election,
“Result not Published yet” Message will be displayed. The result comes with their party symbol on the top of the graph representing the percentage of vote obtained by each candidate.
“Result not Published yet” Message will be displayed. The result comes with their party symbol on the top of the graph representing the percentage of vote obtained by each candidate.
3.4.1.1 DATA FLOW DIAGRAMS
Fig 3.1 to Fig 3.4.2 shows various
levels of DFD’s in our project entitled “Online Voting System”.
3.4.2. DATABASE DESIGN
A
database system is an overall collection of different database software
components and database containing the parts viz. Database application
programs, front-end components, Database Management Systems, and Databases.
Normalization
Normalization
is the process of organizing data in a database. This includes creating tables
and establishing relationships between those tables according to rules designed
both to protect the data and to make the database more flexible by eliminating
redundancy and inconsistent dependency. Redundant data wastes disk space and
creates maintenance problems .If data that exists in more than
one place must
be changed , the data must be changed in exactly the same way in all locations.
A buyer’s or promoter’s address change is much easier to implement if that data
is stored only in the buyer’s or promoter’s table and nowhere else in the
database. There are a few rules for database normalization. Each rule is called
a “normal form
Data
structuring is defined through a process called normalization. Data are grouped
in the simplest way possible so that later changes can be made with a minimum
of impact on the data structure.
There are
different forms of normal forms
·
First normal form(1NF)
·
Second normal form(2NF)
·
Third normal form(3NF)
·
Boyce code normal form(BCNF)
·
Fourth Normal
form(4NF)
·
Fifth Normal
Form(5NF)
TABLES
Table 3.4.1 represents Candidatereg
FIELD
|
TYPE
|
KEY
|
Pkicandidate
id
|
int(11)
|
Primary
|
Fkilogin id
|
int(11)
|
|
Candidate
name
|
varchar(40)
|
|
Candidate
address
|
varchar(40)
|
|
cangender
|
varchar(10)
|
|
candidateofbirth
|
Date
|
|
cansymbol
|
varchar(30)
|
|
fkiconstituencyid
|
int(11)
|
Foreign
|
phone
|
bigint(20)
|
|
emailid
|
varchar(15)
|
|
candesc
|
varchar(30)
|
|
status
|
Varchar(10)
|
|
party
|
varchar(20)
|
Table 3.4.2 represents Constituency
FIELD
|
TYPE
|
KEY
|
pksiconstituencyid
|
int(11)
|
Primary
|
fkilocationid
|
int(11)
|
Foreign
|
constituencyname
|
varchar(20)
|
|
candidatenumber
|
int(11)
|
|
voternumber
|
int(11)
|
Table 3.4.3 represents Electiondetails
FIELD
|
TYPE
|
KEY
|
Pkielectiondetailsid
|
Int(11)
|
Primary
|
Fkivoterid
|
int(11)
|
Foreign
|
Fkielectionmasterid
|
int(11)
|
Foreign
|
Status
|
varchar(20)
|
Table 3.4.4 represents Electionmaster
FIELD
|
TYPE
|
KEY
|
Pkielectionmasterid
|
int(11)
|
Primary
|
Electionname
|
varchar(30)
|
|
Fkiconstituencyid
|
int(11)
|
Foreign
|
Terminationdate
|
date
|
Table 3.4.5 represents Location
FIELD
|
TYPE
|
KEY
|
Pkilocationid
|
int(11)
|
Primary
|
Locationname
|
varchar(40)
|
|
Voterno
|
int(11)
|
Table 3.4.6 represents Login
FIELD
|
TYPE
|
KEY
|
Pkiloginid
|
int(11)
|
Primary
|
Username
|
varchar(20)
|
|
Password
|
varchar(20)
|
|
Role
|
varchar(20)
|
|
Status
|
varchar(20)
|
Table 3.4.7 represents Result
FIELD
|
TYPE
|
KEY
|
Pkresultid
|
int(11)
|
Primary
|
fkicandidateid
|
int(11)
|
Foreign
|
Count
|
int(11)
|
|
Termdate
|
Date
|
Table 3.4.18
represents Voterreg
FIELD
|
TYPE
|
KEY
|
Pkivoterid
|
int(11)
|
Primary
|
Fkiloginid
|
int(11)
|
|
Votername
|
varchar(40)
|
|
voteraddress
|
varchar(40)
|
|
Votergender
|
varchar(10)
|
|
Voterofbirth
|
Date
|
|
Voterimg
|
varchar(30)
|
|
fkiconstituencyid
|
int(11)
|
Foreign
|
Fkilocationid
|
int(11)
|
Foreign
|
Phone
|
Bigint(20)
|
|
Emailed
|
varchar(30)
|
|
Voterid
|
int(11)
|
|
Status
|
varchar(10)
|
|
Age
|
int(11)
|
SYSTEM TESTING
AND
IMPLEMENTATION
4.1. SYSTEM TESTING
Testing is the process of executing
a program with the indent of finding any errors. Testing is vital to the success of the system. Without proper
testing hide errors will surface after sometime of use and perhaps
irreversible damage has been done to valuable data. A series of tests
like responsiveness, its value,
stress and security are performed
before the system
is ready for user
acceptance testing. System
testing follows the
logical conclusion that is
all part of the system
are tested and found to be
working properly under
all kinds of situations, and then
the system is achieving its goal
of processing the data perfectly
according to user
rules and requirements.The different
types of testing are given below.
Ø Unit testing
Ø Validation testing
Ø Output testing
Ø User acceptance
testing
4.1.1 UNIT TESTING
It
involves the basic testing
of a piece of
code, the size of
which is often
undefined in practice. During the
unit testing it is
tested to know
whether that particular
unit in the
proper manner as
expecting, if not
appropriate modifications are applied to
get proper outputs
4.1.2 VALIDATION TESTING
At
the conclusion of the
black box testing, s/w is completely
assembled as a package. Interfacing errors
have been uncovered
and correct and
final series of
test, ie validation begins. Validation test
van is defined
with a simple definition that validation succeeds when the
software functions in a
manner that can
be reasonably accepted
by the customer. Thus we
have successfully done
validation testing.
4.1.3 OUTPUT TESTING
After performing
the validation testing, next is the
output testing of
the proposed system. The system cannot be
useful if it not produce required
output. The output displayed
by the system
under consideration will be
compared with the user
needs. Here the output format
is considered in 2 ways, screen format
and printed format. The o/p
format on the
screen is found
to be correct
as the format
was defined in
the design phase according to user needs. As
for the hardcopy
the o/p comes according
to the specification requested
by the user. Here
the o/p testing
does not result
in any correction
in the system. Thus
we have successfully done
output testing.
4.1.4 USER ACCEPTANCE TESTING
It is the key for success of
any system. The system under
consideration is tested for
user acceptance by
constantly keeping in
touch with perspective
system at the
time of development and
making changes whenever
required. This is done with regarding to the input
screen design and output screen
design. Thus we have successfully done user acceptance testing.
4.2. SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION
System implementation is the final
phase that is putting the utility into action. Implementation is the state in
the project where theoretical design turned into working system. The most
crucial stage is achieving
a new successful system and
giving confidence in new system that
it will work efficiently and
effectively. The system is implemented only after thorough checking is
done and it is found working according to the specifications.
System implementation is the final
phase. i.e., putting the utility into action. Implementation is the state in
the project where theoretical design
turned into working system. The most crucial
stage is achieving a new
successful system and giving confidence in new
system that it will work
efficiently and effectively. Implementation is the state in the
project where theoretical design turned into working system. The implementation
stage is a system project in its own right. It
involves careful planning, design ,investigation of the current system and constraints on implementation, design of
methods to achieve change over
and evolution method. Once the planning has been completed the major effort is to
ensure that the programs
in the system
are working properly. At the same time concentrate on
training user staff.
The major
implementation procedures are:-
Ø Test plans
Ø Training
Ø Equipment installation
Ø Conversion
4.2.1:Test plans
The
implementation of a computer
based system requires
that the test data can be
prepared and the
system and its elements
be tested in a structured manner.
4.2.2:Training
The
purpose of training
is to ensure that
all the personnel who are to
be associated with
the computer based system
possesses necessary knowledge skills.
4.2.3:Equipment installation
Equipment
vendors can provide specifications for equipment installation. They usually
work with projects
equipment installation team
is planning for adequate
space, power and light, and
a suitable environment. After a
suitable site has been completed, the
computer equipment can be installed.
4.2.4:Conversion
It is the processes of performing
all of the
operations that result
directly in turnover of the new
system to the
user. Conversion has two parts:-
1.
The
creation of a conversion
plan at the
start of the development phase
and the implementation of
the plan throughout
the development phase.
2.
The
creation of a system
change over plan
at the end
of the development
phase and the
implementation of the
plan at the
beginning of operation
phase.
CONCLUSION &
FUTURE ENHANCEMENTS
5.1 CONCLUSION
By doing this
project we were able to bring a new system for online national voting for our
country. With the advent of
technology and Internet in our day to day life, we were able to offer advanced
voting system to voters both in the country and outside through our Online
voting system.
Top 4 Reasons to Move to the Online Voting Platform
1.
Efficient and Cost Effective
The system offers significant cost benefits over paper
elections in a vote to vote comparison. It saves an organization the cost of
creating, printing and postage, since everything can be handled electronically.
Online elections reduce the use of paper and the amount of work for both the
organization, as well as voters.
2.
Intelligent
The Online Voting Platform offers intelligent ballots, smart
checklist features, vote tallying, tabulation and reporting. These functions
are automatic and do not need to be assigned to personnel in-house.
Additionally, it allows administrators to create rules on ballots so that
voters cannot cast invalid votes, nor do they need to be checked while
counting.
3.
Save Time and Resources
Online voting system drastically reduces the time required to
set up and conduct elections. There is no excess time required to create paper
ballots, set up paper ballots for printing, wait for the printing to be
completed, or wait for ballots to be filled out and returned.
4.
Easy and convenient
The Online Voting Platform offers the easiest and most
convenient method for administrators and voters alike. For administrators, the
process of setting up a ballot and conducting an election is simple and
manageable.
The
other advantages that the system offers are:
•
Efficient data storage.
•
Accuracy, real-time response and user friendliness.
•
Intelligent Management
5.2
FUTURE ENHANCEMENTS
The Online
Voting System(OVS) platform can be made more secure by using the following
methods
§ Password Changing
§ Fingerprinting
§ Cornea Detection
The
password used by the user to vote is provided by the administrator. In the
future the user can be given the privilege of changing the password. So it
helps to increase the security of the system. The other two methods that can be
used are cornea detection and fingerprinting. But here the problem is that it
decreases the scope of the platform because these systems need some electronic components
to implement. So it will avoid the users privilege to cast the votes at their
fingertips. But it can guarantee that fake voting will be impossible.
The OVS system can be used for different elections.
In this project we had done election for a single loksabha constituency. But
this same system can be used in future for conducting different elections like
local body, legislative assembly, loksabha elections for many constituencies
and wards. For eg: In Kerala there are more than 10000 panchayat wards. The
whole election can be conducted using this single platform. The only
requirement is that we need to create the whole voters database.
Results update through SMS.
In
future we can add an SMS query also. ie we wil get the result updates at the time
of counting. To receive the SMS we need to register with our mobile number in
the site.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- Pankaj Jalote. An Integrated Approach to Software Engineering , Third
Edition, Narosa
Publications. A case study approach whereby a project is
Developed through the
course of the book, illustrating different activities of
Software development
- Herbert Schildt – Java 2: The Complete Reference, Fifth Edition. This book
covers all aspect of java programming language.
- Educational Services Study Guide, Learn the basics of JAVA. Sun Micro
System’s
publications.
- Larne Pekowsky, Java Server Pages Covers 2.0,Second Edition ,Pearson
Education.-contains
all the information necessary to start writing JSP.






No comments